OEE Monitoring
OEE
Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE) is a critical performance metric widely employed in production factories to assess the effectiveness of manufacturing processes. OEE provides a comprehensive and holistic evaluation by considering three key factors: Availability, Performance, and Quality.
By combining these factors, OEE offers valuable insights into the overall performance of manufacturing equipment. It serves as a powerful tool for identifying areas of improvement, minimizing downtime, optimizing production speed, and enhancing product quality. Utilizing OEE in production factories enables businesses to streamline operations, maximize resource utilization, and ultimately achieve higher levels of productivity and efficiency.
IIoT Architecture
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies and solutions into industrial processes and environments. It involves connecting industrial devices, machinery, and systems to the network to collect, exchange, and analyze data, with the ultimate goal of improving efficiency, productivity, and overall operational performance.
The following figure illustrates the comprehensive 4-layer architecture of IIoT. Each layer in this well-defined framework plays a crucial role in facilitating seamless integration and efficient functioning of interconnected industrial devices.

The first layer, Perception Layer, encompasses the physical devices and sensors responsible for data acquisition. IIoT relies on sensors and devices that can gather data from the physical world. These sensors may measure parameters like temperature, pressure, humidity, vibration, and more. They act as the eyes and ears of the industrial system.
Moving up the hierarchy, Network Layer manages the secure and reliable transfer of data between devices. IIoT devices are connected to the internet or network, enabling them to transmit data in real-time. This connectivity allows for seamless communication between devices, systems, and centralized platforms. Various communication protocols are used to facilitate data exchange, including MQTT, CoAP, and HTTP, among others. Furthermore, Given the sensitive nature of industrial operations, IIoT implementations prioritize robust cybersecurity measures to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other potential threats.
Finally, Application Layer resides at the top, providing a user-friendly interface for monitoring and controlling industrial processes. IIoT enables predictive maintenance by monitoring the health and performance of industrial equipment. This helps in identifying issues before they lead to equipment failure, reducing downtime. IIoT facilitates real-time tracking of assets, materials, and products in the supply chain, enhancing visibility and efficiency. Process Optimization: By analyzing data from various stages of production, IIoT can optimize manufacturing processes, improve energy efficiency, and reduce waste.
In summary, Industrial IoT transforms traditional industries by introducing connectivity, data analytics, and automation, leading to more efficient, cost-effective, and adaptive industrial processes. It plays a crucial role in the ongoing evolution of smart factories.
Data Gathering
Checking or counting products in production lines involves deploying a combination of hardware and sensors to collect, process, and transmit data. These components play a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency, quality, and safety of manufacturing operations. Some of the hardware commonly used are PLC, sensor, camera, communication networks, HMI and other industrial IoT hardware.
Various sensors may be used in the production lines like proximity sensors, photoelectric sensors, and vision systems as shown in the figure. Proximity sensors detect the presence or absence of an object without physical contact which is used for object detection, presence sensing, and counting items on the production line. Photoelectric sensors use light beams to detect the presence, absence, or distance of objects that are commonly employed for detecting product position, verifying presence, and measuring distances. Vision systems use cameras and image processing to capture and analyze visual data which is useful in product inspection, quality control, and tracking the movement of items on the production line.



Industrial cameras are ruggedized cameras designed for use in harsh industrial environments. They are equipped with features such as high resolution, high-speed imaging, and compatibility with machine vision algorithms. They capture visual data from the production line and are often integrated with machine vision systems for tasks such as quality control, defect detection, and product tracking.
SFP
In developing SFP (Smart Factory Planning), our approach embraces the advantages of open-source and cross-platform technologies, so we are committed to delivering innovative and accessible software solutions that meet the diverse needs of our users.
Furthermore, efficiency can be integrated into your operations with our cutting-edge Software as a Service (SaaS) solution. Our platform offers a scalable, user-friendly interface, providing a streamlined approach to software access and management. Experience the benefits of cloud-based solutions, from enhanced collaboration to real-time updates, ensuring your business stays agile and ahead in this dynamic digital landscape.
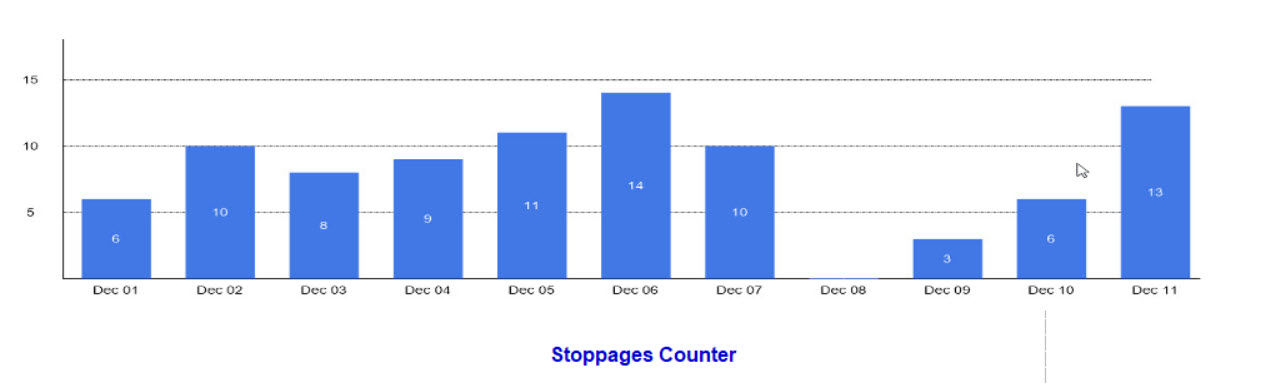
To enhance OEE monitoring in a more intuitive manner, various graphical representations such as bar and harmonic diagrams are available as illustrated in the following figure. These visual aids offer a clearer depiction of workflow and information pertaining to stoppages. Additionally, other displayed items have been utilized including product volume, longest non-stop time, number of stoppages, average step length, down-time, value adding time and ect.
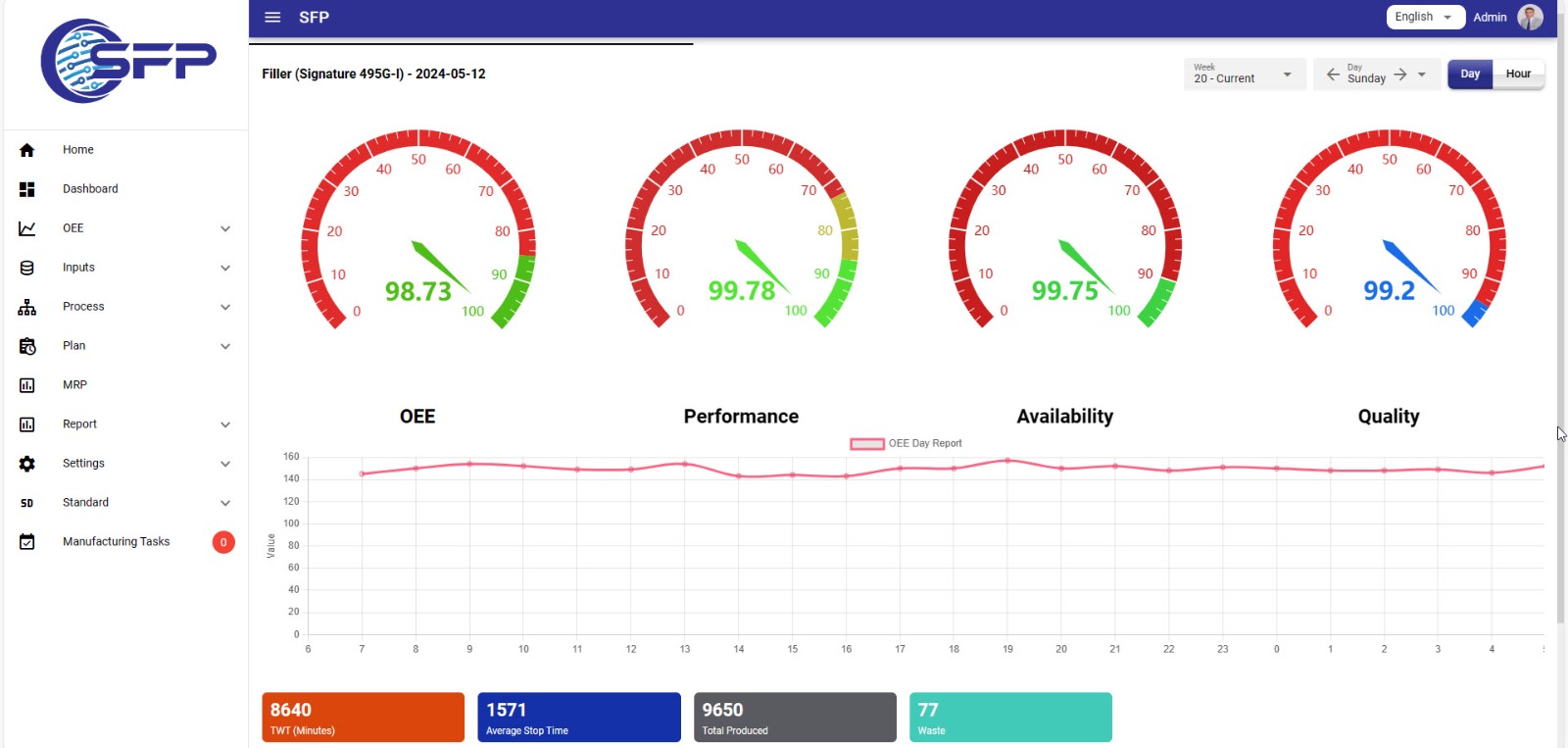
Furthermore, automatic calculation of OEE is designed as shown in the figure. It outlines the reasons for stoppages, enabling operators and supervisors to select a suitable one from a range of predefined options.
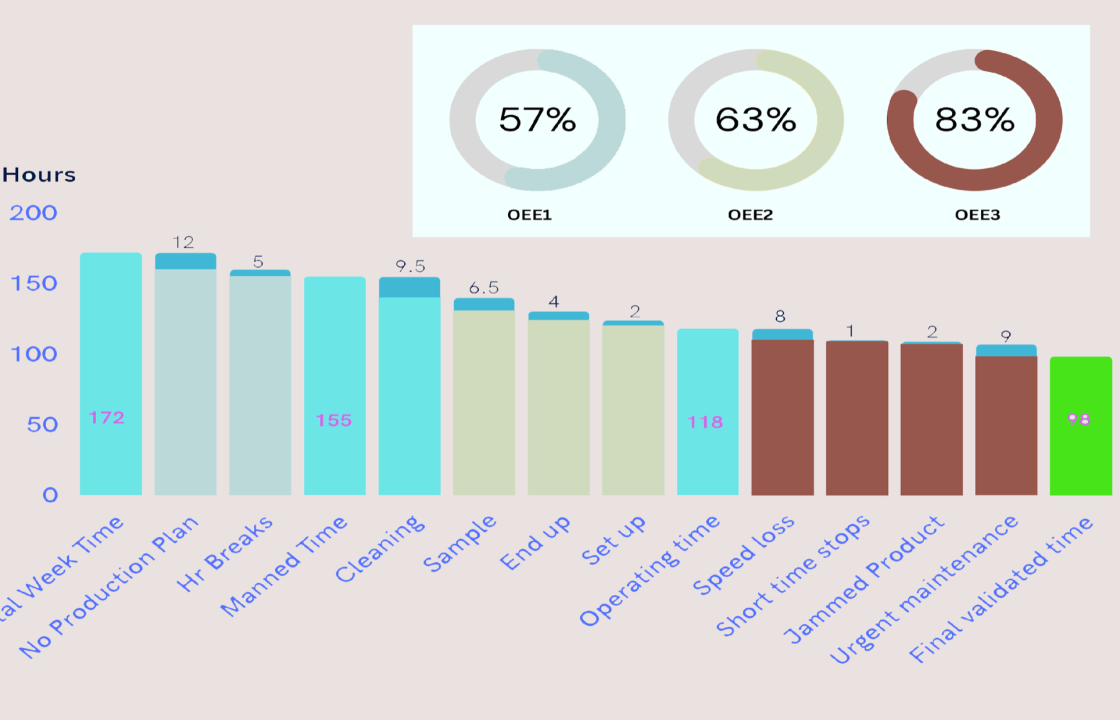
Additionally, a comprehensive breakdown of un-planned stoppages is depicted through an aggregated chart, allowing for a detailed examination to effectively manage shifts and human resource expertise as represented in the figure.
The SFP not only addresses the current challenges in the production processes but also lays the foundation for a more agile, data-driven, and adaptive manufacturing environment. By seamlessly connecting machinery, processes, and data analytics, we envision a substantial increase in production efficiency and a notable improvement in OEE, leading to tangible benefits for our organization.
As we embark on this journey towards a smarter and more efficient production ecosystem, the commitment to excellence and continuous improvement embedded in the SFP aligns seamlessly with our organizational goals. We are confident that the proposed system will not only meet but exceed expectations, ushering in a new era of productivity and competitiveness.
We eagerly anticipate the opportunity to collaborate on the implementation of the Smart Factory Platform, fostering a culture of innovation, efficiency, and sustainable growth.
